
ICARUS ARMOR NEXT GEN is one of 14 leading experiments selected for the ISS and is already delivering its first valuable results
This highly innovative project, selected by the Ministry of Transport for Aleš Svoboda’s historic mission to the International Space Station, is already delivering its first valuable results. The research team presents an analysis of stress biomarkers from saliva samples collected from participants in an experiment conducted under the unique conditions of the Zero G Mission. Immediately after a series of parabolic maneuvers simulating weightlessness, saliva samples were taken from 13 male and 13 female cadets to determine the presence of acute stress biomarkers. The initial results are very promising and pave the way for the creation of the very first scientific dataset of its kind, focused on the effects of microgravity on young astronauts in training.
The analysis was conducted using a prototype photolysis reactor developed by the company Lightly Technologies (Brno, CZ). The reactor uses UVC light to break down components of the original sample, generates new compounds (photo products), and simultaneously performs the corresponding spectral analysis. The samples were chemically processed, measured, and analyzed at the Faculty of Chemistry, Brno University of Technology (FCH BUT), and at the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Mendel University in Brno (DCB MENDELU).
For each analyzed subject, three types of samples were available. The first sample represented a relaxed state, the second corresponded to an immediate stress response, and the third reflected the recovery phase after the stress exposure. For all samples, time-resolved changes in photolysis spectra were obtained. These changes were then described using metrics that best captured the spectral variations during photolysis.
Based on these metrics, two scores were derived:
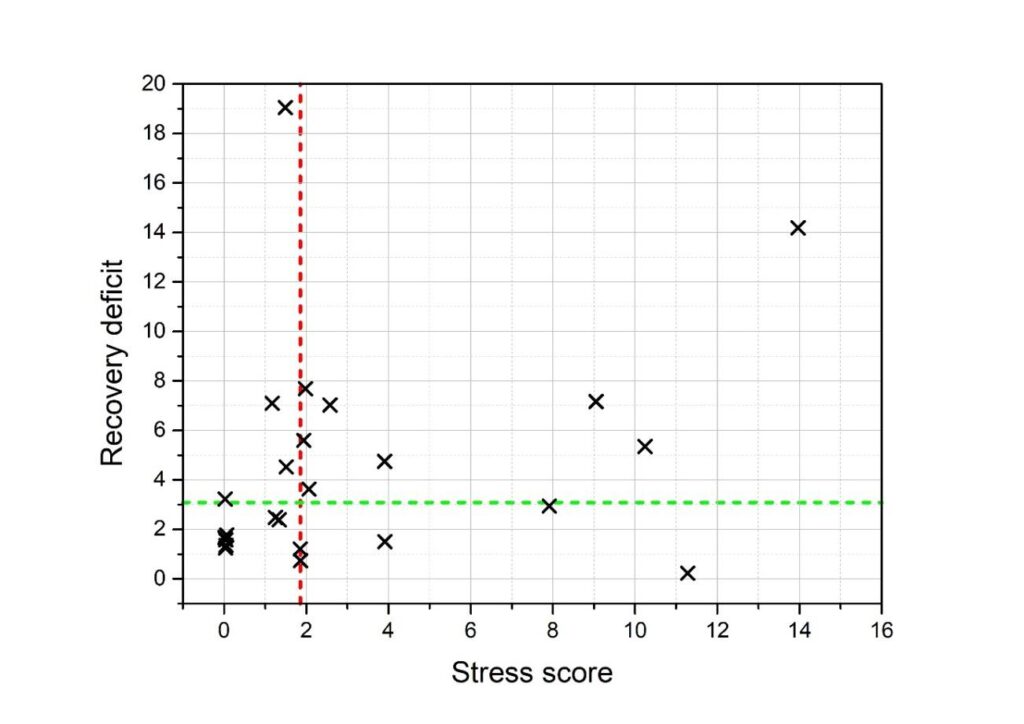
- the Stress Score, reflecting the difference between the stress and relaxed states, and
- the Recovery Deficit, indicating the deviation between the relaxed state and the post-stress recovery state.
These constructed scores reflect how a given subject responds to stress and how their recovery unfolds.
The accompanying scatter plot shows both scores for an anonymized group of subjects. Low values of both the Stress Score and the Recovery Deficit indicate resilient individuals. The higher the Recovery Deficit, the poorer the subject’s recovery process.
Since all subjects were exposed to identical conditions, the data are supplemented with the median values for both the Stress Score and the Recovery Deficit. This allows classification of subjects into four quadrants:
- Quadrant I (top right): high stress, high recovery deficit → high-risk group
- Quadrant II (top left): low stress, high deficit → potential recovery dysfunction
- Quadrant III (bottom left): low stress, low deficit → resilient individuals
- Quadrant IV (bottom right): high stress, low deficit → stress-resistant individuals
It should be noted that this is a pilot measurement conducted on a specific group of subjects. Therefore, any conclusions about individual cases should be confirmed through long-term monitoring. It is essential to characterize the interindividual biological variability of the relaxed state for each subject over time. In addition, extended monitoring of the recovery phase is planned in order to determine the time point at which the Recovery Deficit approaches zero.

Lukáš Nejdl (Lightly Technologies) and Filip Mravec (FCH BUT) analyzing samples in the laboratories of BUT.
This experiment is part of broader preparations for the planned mission of the Czech astronaut to the ISS, with the specific aim of developing a personalized digital twin model to predict astronauts’ cognitive performance under cumulative stress. The project involves Czech companies UptimAI and Lightly Technologies, as well as members of the CAERPIN consortium: the Faculty of Chemistry (FCH) and the Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Communication (FEEC) of Brno University of Technology, and Mendel University in Brno.